Heartburn and acid reflux are common digestive issues that many people experience at some point in their lives. While they may seem like temporary annoyances, they can lead to long-term health problems if not properly addressed. Understanding what causes heartburn and acid reflux, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing how to treat them can help you manage these conditions more effectively.
What is Heartburn and Acid Reflux?
Heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest that often occurs after eating, while acid reflux refers to the backward flow of stomach acid into the esophagus. This reflux can irritate the lining of the esophagus and lead to symptoms like a sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and even regurgitation of food or liquid.
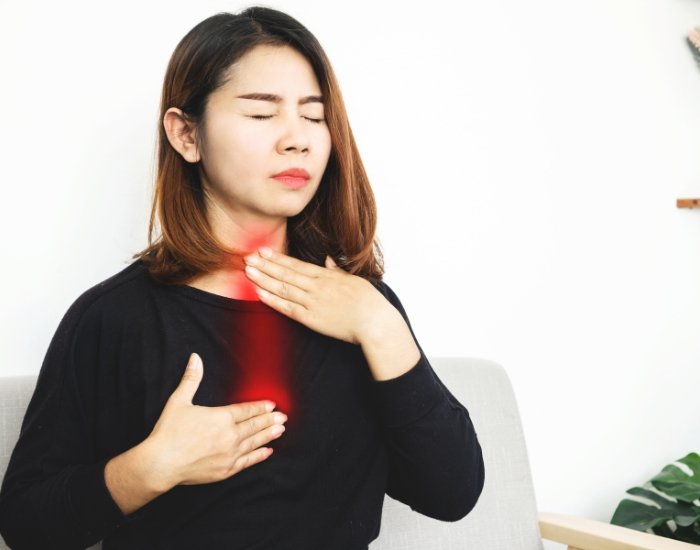

Although heartburn and acid reflux are related, they are not always the same. Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux, and acid reflux can occur without the sensation of heartburn. When acid reflux happens frequently or becomes chronic, it is known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a more serious condition that requires medical attention.
Causes of Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Several factors contribute to heartburn and acid reflux. The most common cause is a weakened lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a muscle that normally prevents stomach acid from flowing backward into the esophagus. When the LES is relaxed or weakened, acid can easily flow back up into the esophagus.
Other factors that can trigger heartburn and acid reflux include:
- Overeating: Eating large meals or lying down right after eating can put pressure on the LES and promote reflux.
- Certain foods and drinks: Spicy foods, citrus, chocolate, coffee, and alcohol can all irritate the esophagus and trigger acid reflux.
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, can put pressure on the stomach, causing acid to back up into the esophagus.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and the physical pressure of the growing uterus can contribute to acid reflux.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the LES and reduces saliva production, both of which can lead to acid reflux.
Symptoms of Heartburn and Acid Reflux
The symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux can vary in severity and frequency. Common signs include:
- A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating or when lying down
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid into the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or the sensation of food being stuck in the throat
- A persistent cough or hoarseness
- A bitter or sour taste in the mouth, especially in the morning
In more severe cases, GERD can cause damage to the esophagus, leading to complications such as ulcers, narrowing of the esophagus, and even an increased risk of esophageal cancer.
Treatment and Management
Managing heartburn and acid reflux often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgery. Here are some strategies that can help alleviate symptoms:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Making certain adjustments to your daily habits can greatly reduce the frequency and intensity of acid reflux symptoms. These include:
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals to avoid overloading the stomach
- Avoiding trigger foods such as spicy dishes, citrus, chocolate, and caffeinated beverages
- Not lying down immediately after eating—wait at least two to three hours before reclining
- Elevating the head of your bed to prevent acid from flowing back into the esophagus while sleeping
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the stomach
2. Medications
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medications can help control acid reflux symptoms. Over-the-counter antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are commonly used to reduce stomach acid and provide relief from heartburn. In some cases, stronger medications or prescription-strength treatments may be necessary.
3. Surgical Options
For individuals with severe GERD or those who don’t respond to other treatments, surgery may be an option. The most common surgical procedure is fundoplication, which involves wrapping the top of the stomach around the LES to prevent acid reflux. Another procedure called the LINX device implantation involves placing a small ring of magnetic beads around the LES to help it stay closed.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional heartburn or acid reflux may be manageable with over-the-counter medications and lifestyle changes, chronic or severe symptoms should not be ignored. Persistent acid reflux can lead to complications such as esophagitis, ulcers, and a condition called Barrett’s esophagus, which can increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
If you experience frequent heartburn, difficulty swallowing, or any of the other symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to seek medical advice. Your healthcare provider can help determine the best course of treatment based on your specific condition and needs.
Final Thoughts: Take Action to Manage Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Heartburn and acid reflux are common, but they shouldn’t be dismissed as a minor inconvenience. By recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes, you can take proactive steps to manage your condition and prevent more serious health issues down the road. If you experience chronic heartburn or acid reflux, don’t hesitate to consult the expert physicians at United Gastroenterology Assoc. PLLC. Our team is here to provide personalized care and help you find the right treatment plan to improve your digestive health.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. It should not be used to diagnose or treat any health condition. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and treatment of any symptoms or medical concerns.